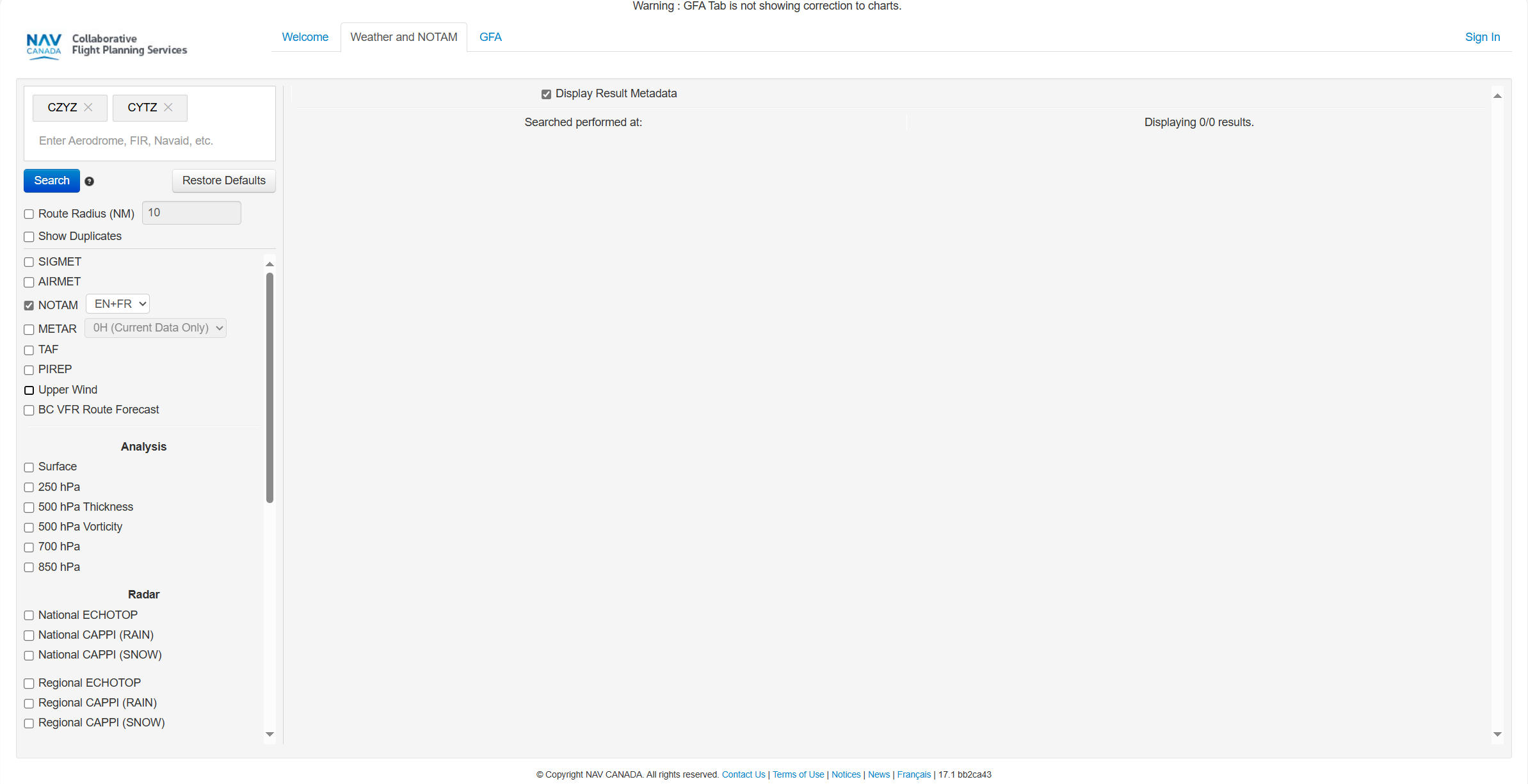
Use the Flightmap to explore and visualize geozones applicable to your category of operation. Click Flightmap in the left sidebar to access the map.
1 - Search Bar
2 - Display Mode
3 - Distance Calculator:
4 - Move the map:
5 - Zoom the map:
6 - Layer on/off
The map layers are a geometric representation of areas that RPAS pilots need to be aware of when planning an operation. Areas filled with red are prohibited. Areas filled with yellow require additional caution due to other air traffic. Areas filled with orange require permission from NAV CANADA, Parks Canada, the Department of National Defence, an airport operator, Penitentiary Authorities or any other specified user agency.
The following map layers are visible for all types of operations:
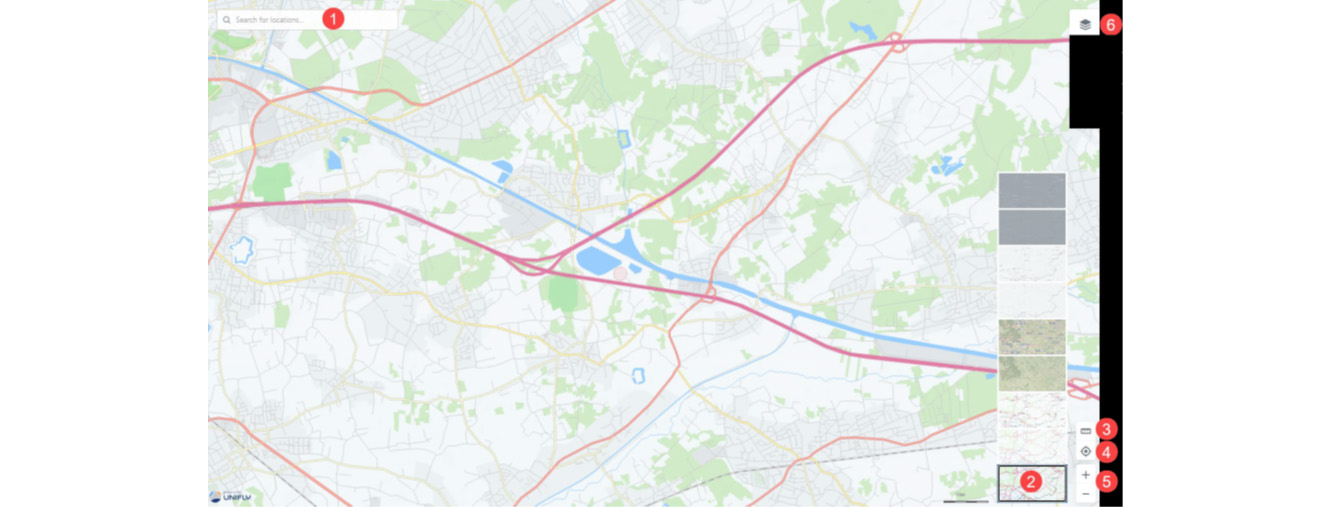
Information about airspace geozones is displayed by selecting a location on the map in the Map window. The selected location is marked with the symbol.
Selected location outside of a geozone:
Selected location is within a geozone:
In NAV Drone, geozones are used to indicate volumes of airspace that have a specific purpose or use within Canada’s airspace. They are displayed on the map to allow operators to:
Additionally, geozones can be used to denote conflicting operations with other RPAS operators. The section below shows examples of the types of geozones operators can expect to see in NAV Drone. When viewing the map in NAV Drone, click a geozone at any time to view detailed information about it.
NAV CANADA grids denote controlled airspace where air traffic control is provided by NAV CANADA.
Grids are displayed when the selected Category of Operation is Advanced or SFOC. Any RPAS operation that overlaps with a portion of the grid requires authorization from NAV CANADA. See Operation Planning and Permission Requests.
Controlled airspace geozones are controlled by NAV CANADA or the Department of National Defence. Advanced operations require authorization from the controlling agency. Basic operations are not permitted. Micro drone operation are permitted and do not require authorization from controlling agency.
Delegated airspace geozones are denote areas where air traffic control is delegated to the FAA due to the proximity of the Canada-US border.
RPAS Restricted Airspaces geozones are located over areas where RPAS operations are not permitted in accordance with the Designated Airspace Handbook (DAH); see the NAV CANADA publications website for additional information.
Certified aerodromes, also called airports, and are typically used by air carriers for scheduled passenger service and are represented by a circle with 3NM radius for the airport center.
Certified heliports are typically used by multi-engine helicopters taking-off or landing at hospitals, commercial helicopter operators or similar.
Registered aerodromes are small airfields with low aviation traffic. For Basic and Advanced RPAS operations, these geozones appear as long ‘racetrack’ shapes representing established traffic patterns, oriented in the same direction as the runways.
For Micro drone operations, these geozones appear as 3NM radius circles on the map.
Registered water aerodromes are represented by 3NM radius circles on the map. RPAS operators need to use caution in these areas since they may encounter amphibious aircraft operating within of water aerodrome geozones.
Registered heliports geozones are represented by a circle with a radius of 1 NM.
Military aerodromes and heliports geozones will appear as a circle showing the 3NM radius from the aerodrome/heliport center. RPAS operators will need to obtain permission from the Department of National Defence to operate within the aerodrome/heliport geozone. The contact information can be found by clicking on the geozone.
Class F Restricted airspace is represented by geozones where flight operations, including RPAS operations are not permitted unless specifically authorized by the responsible user agency.
Class F Danger airspace is a special use airspace designated with identifiers starting with CYD. RPAS operations are not permitted in Class F Danger geozones unless authorized by the responsible user agency.
Class F Advisory airspace geozones indicate areas where there is an increased risk of encountering crewed aviation. It is recommended that RPAS operators used caution in these areas.
Temporary No Drone Zone geozones are typically put in place under special circumstances where RPAS operations are not permitted unless they are associated with the user/controlling agency. Contact information is available by clicking the geozone.
Park geozones are areas designated by the Federal Government as National Parks of Canada and may not allow RPAS operations. Check with the park authority to determine if RPAS operations are permitted.
A NOTAM is a memo that communicates important information to all personnel involved in flight operations concerning potential hazards, changes to airspace, aeronautical facilities, services, procedures, and so on.
Since RPAS are considered aircraft that operate in Canadian airspace, operators and pilots should be aware of NOTAMs in their area of operation.
NAV Drone aims to display all relevant NOTAM geozones that affect RPAS operations so that pilots may effectively plan their operations and act accordingly.
The following geozones are applicable to lower-risk BVLOS operations (Level 1 Complex):
The ARC is a qualitative categorization that represents the intrinsic risk of an RPA encountering another aircraft during a planned operation before mitigations. ARC-A, ARC-B, ARC-C, ARC-D generally define airspace with increasing risk of midair collision. Lower risk BVLOS operations are only possible in ARC-A, ARC-B, or ARC-C. The requirements for tactical mitigations such as Detect and Avoid systems or Visual Observers vary depending on the ARC classification.
ARC-A is generally defined as atypical airspace (CYR/CYD/NDA). Lower-risk BVLOS operations at 400 ft AGL or less are only possible here with Visual Observers in accordance with Standard 923 (performance requirements for visual observers) or a DAA system that meets Standard 922.10 (performance requirements for DAA systems based on Risk Ratio)with a Risk Ratio of 1.0 or less.
ARC-B is generally defined as uncontrolled Class G airspace at 400 ft AGL or less that is at least 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) away from aerodromes, airports and heliports published in the CFS/WAS. Lower-risk BVLOS operations at 400 ft AGL or less are only possible here with Visual Observers in accordance with Standard 923 (performance requirements for visual observers) or a DAA system that meets Standard 922.10 (performance requirements for DAA systems based on Risk Ratio) with a Risk Ratio of 0.66 or less.
ARC-C is generally defined as uncontrolled Class G airspace at 400 ft AGL or less that is at least 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) away from aerodromes and heliports published in the CFS/WAS, that has controlled airspace (extending to 1500 ft AGL or less) above it. Class F Advisory airspace (CYA) is also considered as ARC-C. Lower-risk BVLOS operations at 400 ft AGL or below are only possible here with Visual Observers in accordance with Standard 923 (performance requirements for visual observers) or a DAA system that meets Standard 922.10 (performance requirements for DAA systems based on Risk Ratio) with a Risk Ratio of 0.33 or less.
ARC-D is generally defined as controlled airspace at 400 ft AGL or below, or airspace within 5 nautical miles (9.3 km) from aerodromes, airports and heliports published in the CFS/WAS.
NAV Drone uses population density data to help visualize areas where lower-risk BVLOS operations may be planned. Lower-risk BVLOS operations conducted with a small RPA are prohibited over densely populated areas (25 or more people/km2). Lower-risk BVLOS operations conducted with a medium RPA are prohibited within one kilometer of a populated area (> 5 people / km2). NAV Drone uses data from the 2021 census to visualize population density. As per regulations, you are responsible for validating the population data by performing a site survey and identifying any local events, gatherings, and other places where people may congregate, such as concerts, festivals, sports tournaments.
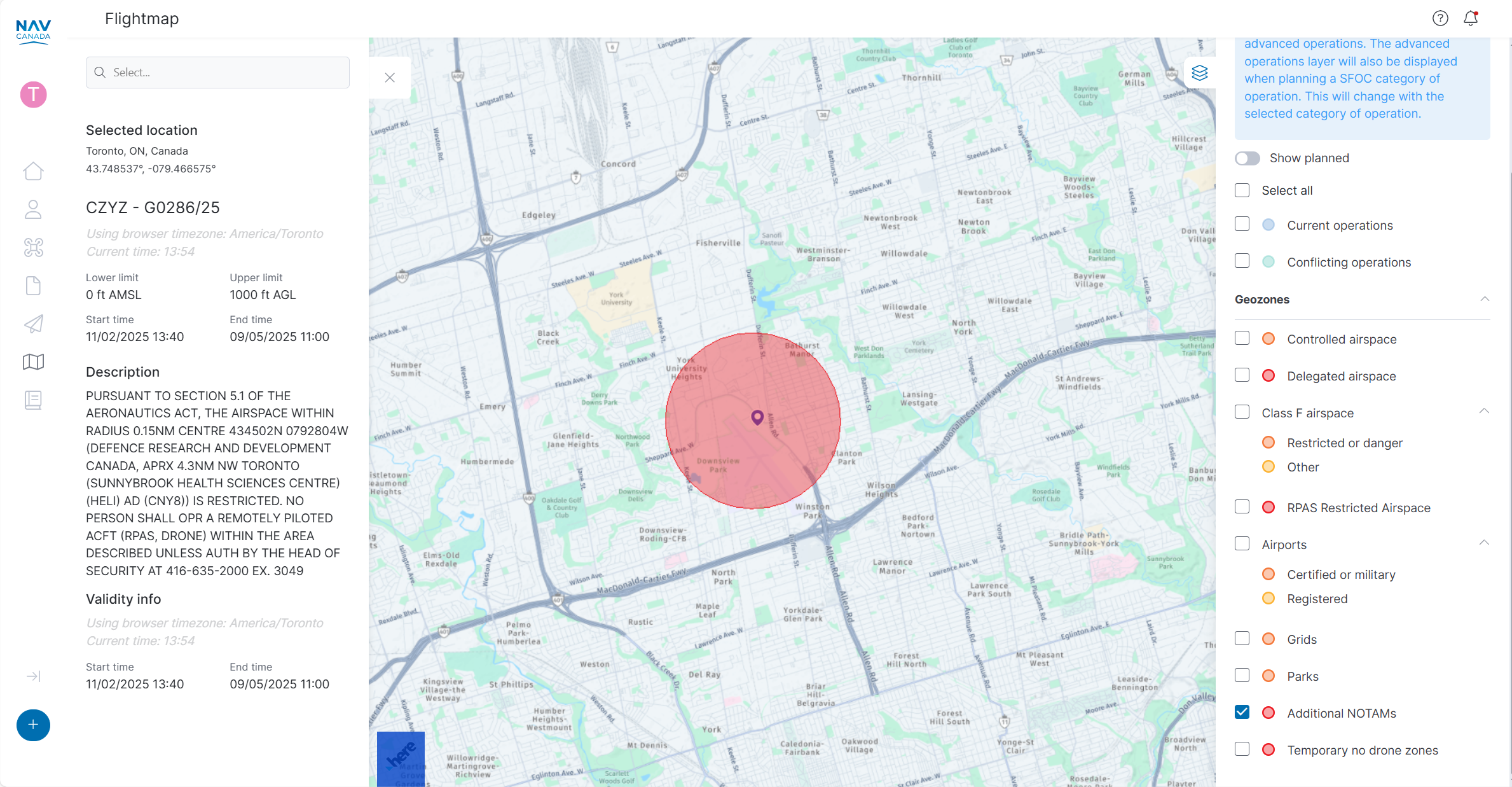
A NOTAM will appear as a circular zone on the NAV Drone map (either in Flight map or the operation planning map screens) and indicates the boundary of an airspace that is affected by the NOTAM. Clicking the NOTAM geozone opens a description of the NOTAM itself on the left-hand side of the screen.
In the example below, a red circle centered East-North-East of London, ON indicates that the airspace in this area is under the effect of a NOTAM (known as the Area of Influence of the NOTAM).
Clicking on the circle itself shows the information panel to the left, which provides the details of the NOTAM, including:
NOTE: Sometimes, a NOTAM will appear as a large circular area even though the NOTAM may restrict a smaller area; the example below is commonly used to restrict airspace for Forest Fires, and the Area of Influence will always be a circle that encloses or may be slightly larger than the airspace that is restricted by the NOTAM.
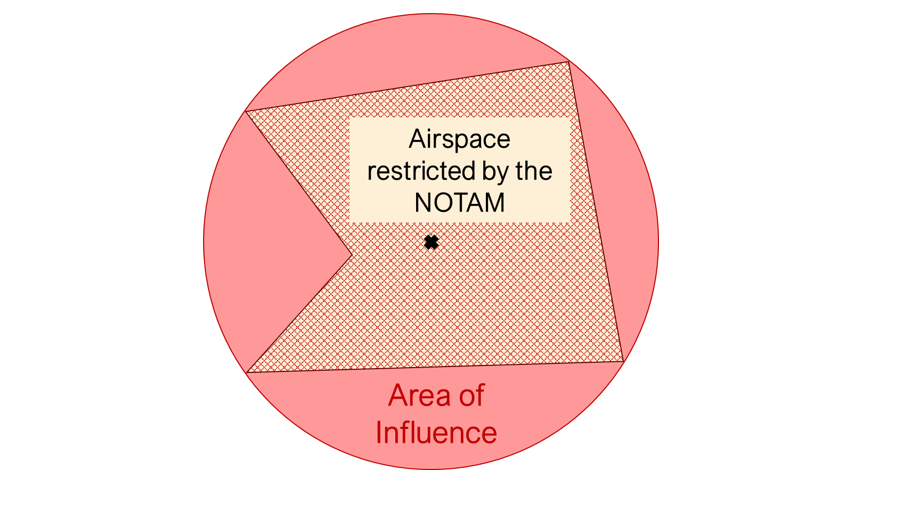
IMPORTANT: If an RPAS operation is affected by a NOTAM, operators must review the full NOTAM information to ensure they are complying with any restrictions or conditions that affects their operation.
The full NOTAM information can be accessed from the NAV CANADA Collaborative Flight Planning Services by searching for NOTAMs for a specific aerodrome or FIR as shown below.